| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
| 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 |
| 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 |
| 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 |
Tags
- 3유형
- 실기
- Kaggle
- 인공지능
- KNN
- GPU
- QGIS설치
- webserving
- DASH
- 딥러닝
- qgis
- 빅데이터분석기사
- 성능
- 공간분석
- Ai
- streamlit
- 2유형
- pytorch
- CUDA
- fastapi
- ㅂ
- dl
- 캐글
- ml 웹서빙
- K최근접이웃
- 공간시각화
- gradio
- 머신러닝
- 1유형
- 예제소스
Archives
- Today
- Total
에코프로.AI
[Python] JSON 데이터 처리관련 본문

JSON이란?
- JavaScrip Object Notation 의 약자
- 데이터를 저장하고 전송하기 위해 사용하는 경량 데이터 교환 포맷
- 텍스트 기반으로 사람이 읽고 쓸수 있으며, 기계가 분석하고 생성할 수 있음
- JSON의 특징
- 간결성
가독성이 좋고, 구조가 간결하여 데이터를 쉽게 이해할 수 있음 - 가독성
사람과 기계 모두가 읽고 쓰기 쉽게 설계되어 있음 - 유연성
객체와 배열을 사용하여 복잡한 데이터 구조를 쉽게 표현할 수 있음 - 호환성
대부분의 프로그래밍 언어에서 JSON을 쉽게 파싱하고 생성할 수 있는 라이브러리를 제공함.
- 간결성
JSON의 기본구조
- 키-값 쌍으로 데이터를 표현화며, 중첩된 구조를 가질 수 있음
- 주요 요소
- JSON 객체
- 중괄호 '{}'로 감싸고, 키-값 쌍으로 구성
- JSON 객체
{
"name" : "John",
"age" : 30
}-
- JSON 배열
- 대괄호 '[]'로 감싸고, 쉼표로 구분 된 값들의 리스트
- 배열의 인덱스는 0부터 시작
- JSON 배열
[ "apple", "banana", "cherry" ]- JSON 데이터 타입
- 기본자료형
- 객체(사전), 배열(리스트), 문자열, 숫자, Boolean, null
- Null은 빈 값을 나타냄
- 리스트 마지막에 쉼표가 있으면 안됨.
- 객체의 키 값은 반드시 문자열
- 기본자료형
obj = """
{"name" : "Wes",
"places_lived" : ["", "", ""],
"pet" : null,
"siblings" : [ {"name" : "Scott", "age" : 25, "pet" : "Zuko"},
{"name" : "Katie", "age" : 33, "pet" : "Cisco"} ]
}
"""JSON 예제코드
# json 라이브러리 사용관련 선언
import json
JSON 객체 생성
obj = """
{"name" : "Wes",
"place_lived" : ["United States", "Spain", "Germany"],
"pet" : null,
"siblings" : [{"name" : "Scott", "age" : 25, "pet" : "Zuko"},
{"name" : "Katie", "age" : 33, "pet" : "Cisco"}]
}
"""print(type(obj))
print(obj)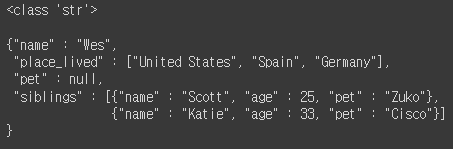
JSON 데이터 읽고 쓰기
json.loads()
- json문자열을 파이썬 객체로 디코딩
result = json.loads(obj)
print(type(result)) # <class 'dict'>
print(result)
print('name : ', result['name'])
print('place_lived : ', result['place_lived'])
print('pet : ', result['pet'])
print('siblings : ', result['siblings'])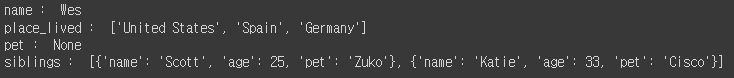
print(result['siblings'][1]['name'])
print(result['siblings'][1]['age'])
print(result['siblings'][1]['pet'])
json.load()
- 파일에서 읽은 json 데이터를 파이썬 사전 객체로 디코딩
- 아래 형식의 sample.json 파일 생성
{"name" : "Wes",
"place_lived" : ["United States", "Spain", "Germany"],
"pet" : null,
"siblings" : [{"name" : "Scott", "age" : 25, "pet" : "Zuko"},
{"name" : "Katie", "age" : 33, "pet" : "Cisco"}]
}json_file_path = 'sample.json'
with open(json_file_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as file:
result2 = json.load(file)
print(type(result2))
print(result2)print(result2['siblings'][0]['name'])
print(result2['siblings'][0]['age'])
print(result2['siblings'][0]['pet'])result2['siblings'][1]['age'] = 30 # 나이를 30으로 변경
print(result2['siblings'])
json.dumps()
- 파이썬 사전 객체를 json 문자열로 인코딩
new_result = json.dumps(result)
print(type(new_result))
print(new_result)
# a python object (dict)
x = {
"name" : "John",
"age" : 30,
"city" : "New York"
}
y = json.dumps(x)
print('type(x) : ', type(x))
print('type(y) : ', type(y))
print(y)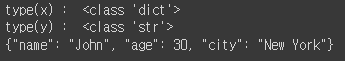
# Python 객체를 JSON 문자열로 변환하고 값을 출력합니다.
import json
print(json.dumps({"name" : "John", "Age" : 30}))
print(json.dumps(['apple', 'banana']))
print(json.dumps(('apple', 'banana')))
print(json.dumps('hello'))
print(json.dumps(42))
print(json.dumps(31.76))
print(json.dumps(True))
print(json.dumps(False))
print(json.dumps(None))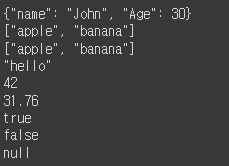
import json
x = {
"name" : "John",
"age" : 30,
"married" : True,
"divorced" : False,
"children" : ("Ann", "Billy"),
"pets" : None,
"cars" : [
{"model" : "BMW 230", "mpg" : 27.5},
{"model" : "Ford Edge", "mpg" : 24.1}
]
}
print(json.dumps(x))
json.dump()
- 파이썬 사전 객체를 json 파일로 인코딩
- indent : 들여쓰기
with open("newsample.json", 'w', encoding='utf-8') as file:
json.dump(result1, file, indent = 4)
pandas.read_json()
- 단순한 데이터 구조의 json 데이터 셋은 DataFrame 으로 변환할 수 있다.
- 복잡한 구조의 json 데이터는 변환불가
- 아래 형식의 sample2.json 파일을 생성한다.
[{"a" : 1, "b" : 2, "c" : 3},
{"a" : 4, "b" : 5, "c" : 6},
{"a" : 7, "b" : 8, "c" : 9}
]
import pandas as pd
data = pd.read_json('sample2.json')
data
DataFrame.to_json()
- DataFrame에 저장 된 데이터를 json으로 저장
print(data.to_json())
print(data.to_json(orient='records'))
pandas.json_nomalize()
- 복잡한 json 데이터는 json_nomalize()를 이용해서 DataFrame으로 변환가능
df = pd.DataFrame(result)
dfprint(df['place_lived'][0][0])
print(df['siblings'][0][0]['name'])# pandas.json_nomalize()
import pandas as pd
import json
with open('sample.json', 'r') as file:
data_dict = json.load(file)
df = pd.json_normalize(data_dict)
print(df)
JSON 실습
json_obj = """
{
"employees": [
{
"name": "홍길동",
"age": 30,
"department": "SW개발부",
"skills": [
"Python",
"JavaScript",
"C++"
]
},
{
"name": "김길동",
"age": 25,
"department": "마케팅부",
"skills": [
"쇼셜미디어마케팅",
"컨텐트 개발"
]
}
]
}
"""import json
import pandas as pddict = json.loads(json_obj)print(type(dict))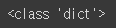
data = dict['employees']
print(data)
print(type(data))
print(type(data[0]))
for employee in data:
print(f'name : {employee["name"]}')
print(f'age : {employee["age"]}')
print(f'department : {employee["department"]}')
print(f'skills : {employee["skills"]}')
import pandas as pd
df = pd.read_json(dict['employees'])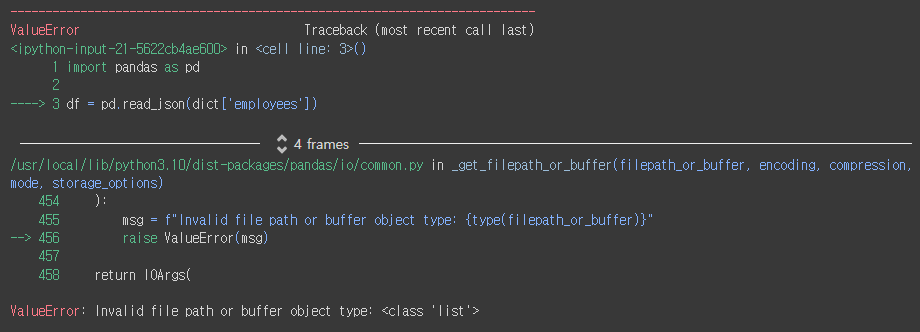
※ 복잡한 형식의 json을 read_json으로 읽으려고 하면 위와 같이 오류 발생함.
json_normalize 로 읽어야 정상 처리 가능
import pandas as pd
df = pd.json_normalize(dict['employees'])
df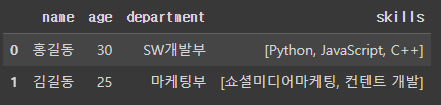
import pandas as pd
df1 = pd.json_normalize(dict)
df1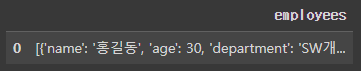
#print(type(df1))
#print(df1)
print(df1['employees'])
print(df1['employees'][0])
print(df1['employees'][0][0])
print(df1['employees'][0][0]['name'])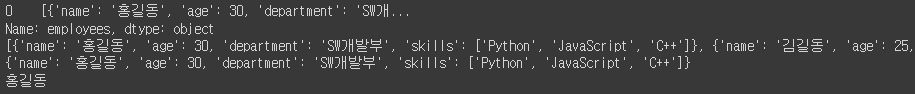
'AI Miscellany' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [데이터분석 협업] - 구글드라이버 & Jupyter & Colab(Feat.GitHub) (3) | 2024.10.10 |
|---|---|
| [GitHub] GitHub으로 협업하기 (1) | 2024.09.28 |
| [GitHub] GitHub 가입 및 기본사용법 (0) | 2024.08.14 |
| [관련도서] 원인과 결과의 경제학 (0) | 2024.05.21 |
| [빅분기] 스터디모임 발표준비 (2024.03.09) - 서포트벡터머신(SVM) (0) | 2024.03.07 |